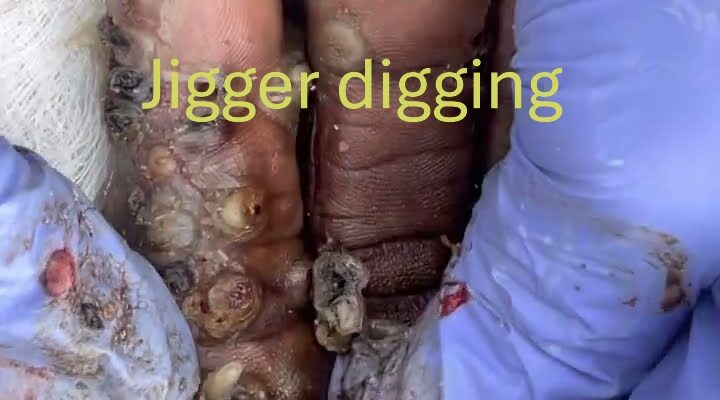
Jigger digging refers to the process of manually removing jiggers (a type of parasitic flea, also known as Tunga penetrans) from the skin, typically from the feet. Jiggers burrow into the skin, particularly between the toes, and lay their eggs, causing pain, inflammation, and potential infection if not treated properly. The term “jigger digging” is used in some regions, particularly in parts of Africa and South America, where jiggers are more common, and it involves carefully digging out the flea using a sterile needle or similar tool.
While this may be a traditional or common practice in certain areas, it is important to note that professional medical care is recommended to prevent complications such as infections or secondary diseases. Proper hygiene, prevention, and early treatment can help avoid the need for this practice.
If you’re referring to how to properly purify or clean the area affected by jiggers or how to prevent or treat jigger infestations, here’s a general guide:
1. Prevention:
- Wear protective footwear: Avoid walking barefoot in areas where jiggers are common, such as sandy or grassy areas.
- Clean surroundings: Keeping living areas clean and free from fleas can reduce the risk of infestation.
- Use insect repellents: In areas where jiggers are common, apply insect repellent to prevent them from attaching to your skin.
2. Treatment (If Infested with Jiggers):
- Soak the feet: If jiggers are already present, soak the feet in warm, soapy water for about 15–20 minutes. This softens the skin and makes it easier to remove the jiggers.
- Disinfect tools: If you need to dig out the jigger, use a sterile needle or small tweezers. Clean the tools with alcohol to prevent infection.
- Remove the jigger: Gently extract the flea from under the skin using the needle or tweezers. Avoid squeezing or forcing it out, as this can cause injury or infection.
- Clean and disinfect the area: After removal, clean the area with antiseptic or an antibacterial solution.
- Apply ointment: To prevent infection and reduce inflammation, apply an antibiotic ointment or a soothing cream.
- Bandage the area: If necessary, cover the affected area with a clean bandage to protect it from dirt and bacteria.
3. Aftercare:
- Monitor for infection: Keep an eye on the site of the jigger removal for signs of infection, such as redness, swelling, or pus. If these occur, seek medical attention.
- Maintain cleanliness: Continue to clean and protect the affected area until it heals completely.
If the infestation is extensive or you are unsure how to properly remove the jiggers, it’s best to consult a healthcare professional for assistance.